A hazardous waste is a waste with properties that make it dangerous or capable of having a harmful effect on human health or the environment. Hazardous waste is generated from many sources, ranging from industrial manufacturing process wastes to batteries and may come in many forms, including liquids, solids gases, and sludges.
The EPA regulates hazardous waste under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) and has developed a regulatory definition and a complex process that identifies specific substances known to be hazardous.
A hazardous waste generator, by regulation, is an entity, by site, whose acts or processes generate a solid waste that is:
- listed in the hazardous waste regulations,
- determined to be a characteristically hazardous, or
- otherwise identified as a hazardous waste.

Hazardous waste generators are categorized by the EPA into three categories, based on the amount of waste produced, and are subject to different levels of regulation:
- Very small quantity generators (VSQGs) – (previously called “conditionally exempt small quantity generators (CESQGs))
- Small quantity generators (SQGs)
- Large quantity generators (LQGs)
The volume of hazardous waste each generator produces in a calendar month determines which regulations apply to that generator.
Authorized Different State Regulations for Hazardous Waste Generators
Some states have been authorized to establish generator categories that are different from those that federal EPA set up. View a list of states that have hazardous waste generator category regulations that differ from the federal regulations and which have the same generator categories.
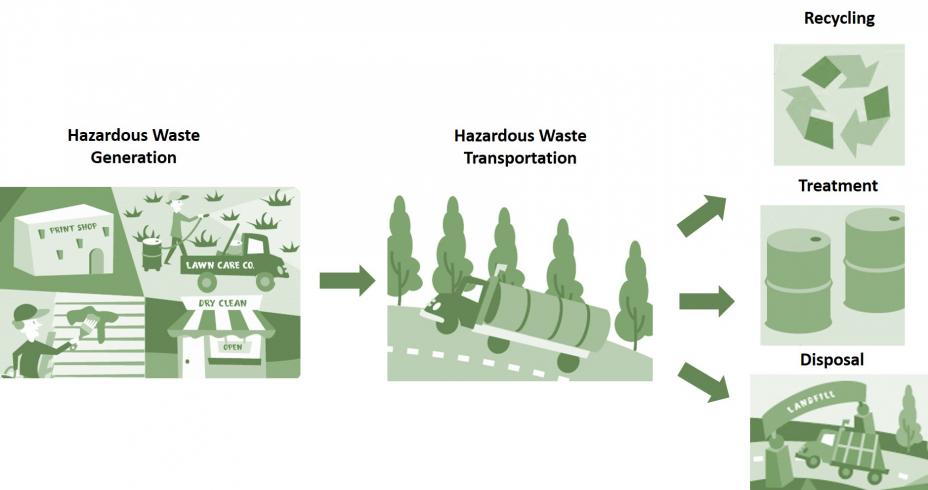
RCRA’s Cradle-to-Grave Hazardous Waste Management System
Hazardous Waste Generator Categories
Very Small Quantity Generators
- Hazardous Waste Generated – Quantity Limits: ≤ 100 kg/month, and ≤ 1 kg/month of acute hazardous waste, and ≤ 100 kg/month of acute spill residue or soil.
- RCRA Training: Training not mandatory – but recommended so employees can recognize and properly manage hazardous wastes and prevent spills.
- 40 CFR 260.14
Small Quantity Generators
- Hazardous Waste Generated – Quantity Limits: >100 kg/month and <1,000 kg/month
- RCRA Training: Basic RCRA training required.
- 40 CFR 262.16 (b)(9)(iii)
- (iii) The small quantity generator must ensure that all employees are thoroughly familiar with proper waste handling and emergency procedures, relevant to their responsibilities during normal facility operations and emergencies.
Large Quantity Generators
- Hazardous Waste Generated – Quantity Limits ≥1,000 kg/month, or >1 kg/month of acute hazardous waste, or >100 kg/month of acute spill residue or soil
- RCRA Training: Full RCRA training Required
- 40 CFR 262.17(a)(7)
- (7)Personnel training.
- (i)(A) Facility personnel must successfully complete a program of classroom instruction, online training (e.g., computer-based or electronic), or on-the-job training that teaches them to perform their duties in a way that ensures compliance with this part.
- (C) At a minimum, the training program must be designed to ensure that facility personnel are able to respond effectively to emergencies by familiarizing them with emergency procedures, emergency equipment, and emergency systems, including where applicable:
- (1) Procedures for using, inspecting, repairing, and replacing facility emergency and monitoring equipment;
- (2) Key parameters for automatic waste feed cut-off systems;
- (3) Communications or alarm systems;
- (4) Response to fires or explosions;
- (5) Response to ground-water contamination incidents; and
- (6) Shutdown of operations.
- (iii)Facility personnel must take part in an annual review of the initial training required in paragraph (a)(7)(i) of this section.
Reference: EPA: Categories of Hazardous Waste Generators
EPA Mandated RCRA Training
The EPA requires all employees that handle hazardous materials in facilities that generate hazardous waste, complete an RCRA training course detailing the RCRA regulatory requirements.
After completing the initial training course, hazardous material professionals are mandated to complete an annual refresher to keep current on the extensive regulatory requirements.
The EPA requires RCRA training for “personnel” [40 CFR 260.10 – Definitions] or “all persons who work at, or oversee the operations of, a hazardous waste facility, and whose actions or failure to act may result in noncompliance” – must complete RCRA training within 6 months of initial hire – and take an 8 hour refresher training course annually [40 CFR 265.16(b) and (c)].

RCRA Civil and Criminal Penalties
For sites subject to the EPA’s Resource and Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) hazardous waste rules – civil and criminal penalties for violations can be harsh.
The EPA and the states verify RCRA compliance with these requirements through a comprehensive compliance monitoring program which includes inspecting facilities, reviewing records and taking enforcement action where necessary.
The RCRA compliance assistance program provides businesses, federal facilities, local governments and tribes with tools to help meet environmental regulatory requirements.
For more info, see the EPA – Criminal Provisions of the RCRA webpage.
